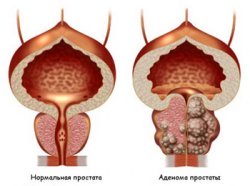
Prostate adenoma (BPH) is the most common tumor in men. It is benign, but its symptoms dramatically worsen the quality of human life.
Treatment of adenoma, as well as treatment of prostatitis individually and should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a urologist!
It is strongly recommended at the first manifestations of an illness to immediately seek advice from a specialist.
Symptoms of manifestation of prostate adenoma:
- rapid urination,
- a weak stream of urine,
- feeling of partial emptying of the bladder,
- straining with urination and leakage of urine after it, etc.
Types of treatment for prostate adenoma
Treatment of adenoma is divided into conservative and surgical:
- Drug therapy is carried out by two groups of drugs: alpha adrenoreceptor blockers, relaxing smooth muscle fibers of the prostate and bladder neck and 5α-reductase inhibitors that block the formation of dihydrotestosterone from testosterone at the prostate level. Drug therapy is long (at least 6 months), has a number of side effects and does not always give a positive result.
Surgical treatment includes open surgery, endoscopic and alternative minimally invasive interventions. - Surgical treatment is clearly recommended for patients with obvious symptoms and the presence of complications (recurrent urinary tract inflammation, recurrent hematuria, etc.), as well as with acute urinary retention and the risk of developing chronic renal failure.
In 95% of cases, adenoma of the prostate gland can be removed endoscopically. Scheduled operation is performed under spinal anesthesia, the patient is hospitalized for 1-2 days. So far, TUR (transurethral resection) of the prostate has been recognized as the “Golden Standard” of the operational benefit, which is successfully performed at the Center for Progressive Medicine “AVICENNA MED”. This access is possible not only partial, but complete removal of the prostate, as well as its dissection.
Learn the prices of urological operations
Adenectomy of the prostate with open access is performed only if it is impossible to have a less traumatic variant. Nowadays, modern minimally invasive interventions have appeared (transurethral vaporization of the prostate by laser, embolization of the prostatic artery, transurethral needle ablation, etc.), but they are generally applicable for small tumor sizes.
Currently, TUR of the prostate remains the most reliable and safe method of treatment. Reduction of clinical manifestations and improvement of urodynamic parameters after TUR of the prostate gland is more noticeable than after other surgical interventions.